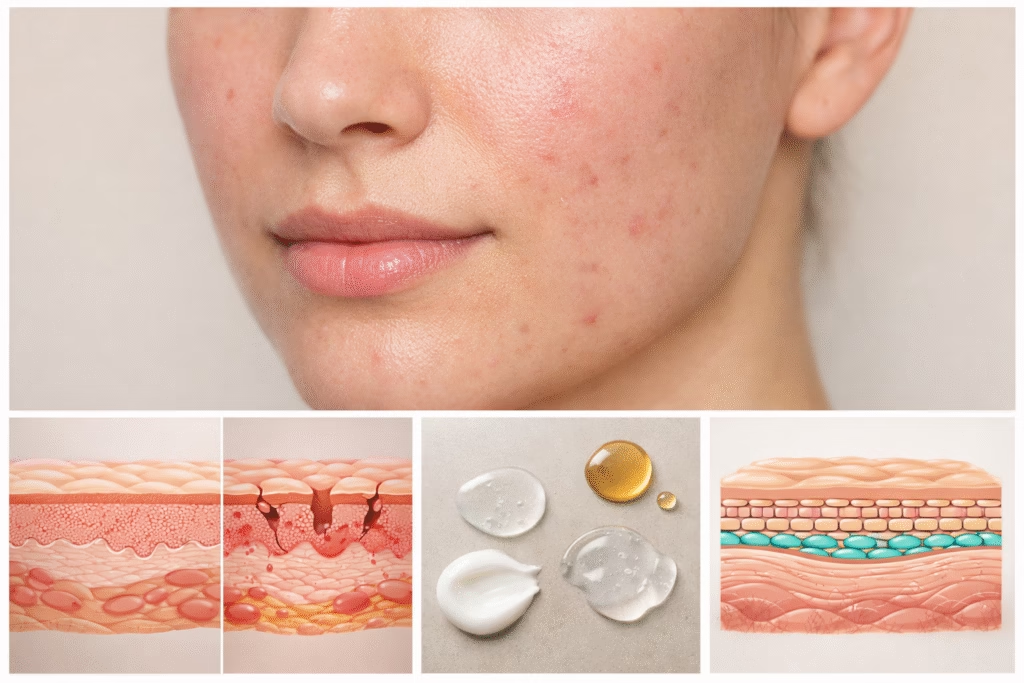
Acne-prone skin often reflects a weakened barrier. Repairing the skin barrier helps reduce inflammation, sensitivity, and breakouts.
This guide explains the skin barrier in simple, science-backed terms and shows you how to repair it correctly without damaging shortcuts.
What Is the Skin Barrier?
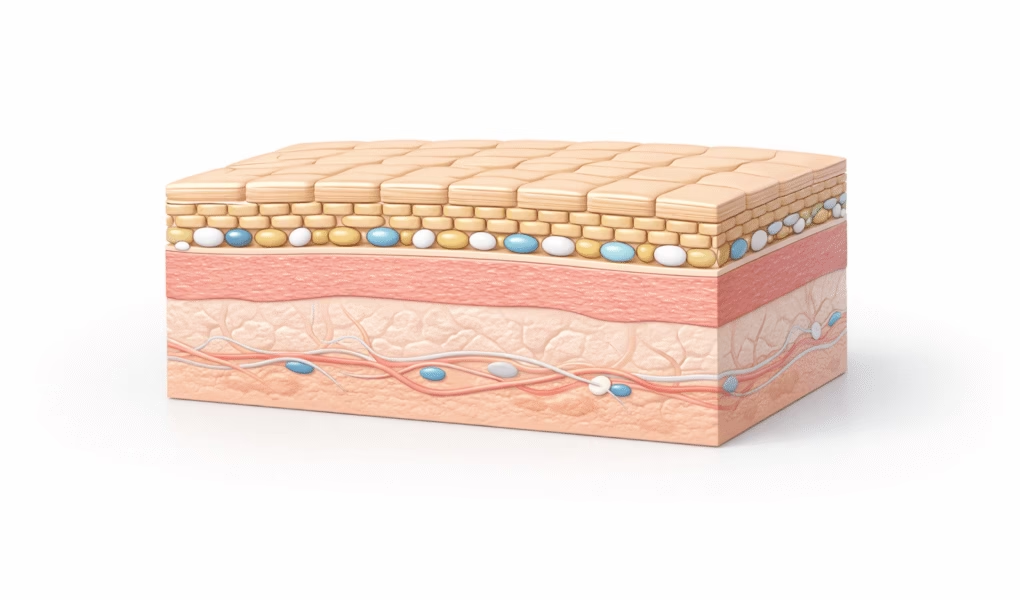
The skin barrier, mainly the stratum corneum, is the outermost layer of the epidermis. It functions like a protective wall made of skin cells held together by lipids such as ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids.
Its primary roles are:
- Protecting skin from pollution, UV rays, microbes, and irritants
- Preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL)
- Maintaining hydration, balance, and resilience
According to AAD, when this barrier is intact, skin remains calm and hydrated. When compromised, even mild products can sting.
Key Functions of the Skin Barrier
A healthy skin barrier:
- Shields against environmental aggressors like pollution and UV radiation
- Locks in moisture and prevents dehydration
- Regulates immune and inflammatory responses
- Maintains smooth texture and even skin tone
- Supports long-term skin health and glow
Without a functional barrier, skincare results become unpredictable.
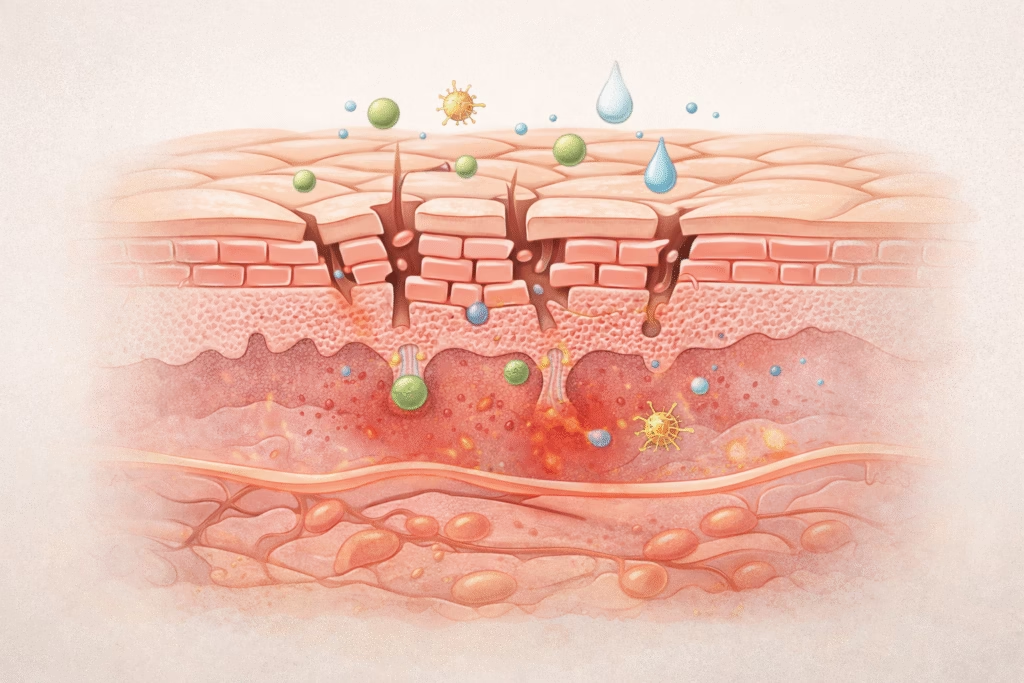
How to Tell If Your Skin Barrier Is Damaged
Barrier damage produces consistent and noticeable symptoms.
Common Signs
- Dry, flaky, or scaly skin
- Redness and inflammation
- Burning or stinging when applying products
- Tightness despite moisturizing
- Sudden breakouts or worsened acne
- Eczema-like rashes or irritation (National Eczema Association)
If your skin reacts to everything, the issue is usually barrier damage, not “sensitive skin.”
What Causes Skin Barrier Damage?
Barrier damage usually comes from repeated stress rather than a single mistake.
- Over-washing or harsh cleansers
- Over-exfoliation with acids or scrubs
- Excessive use of retinoids
- UV exposure and pollution
- Extreme weather, chlorine, dry indoor air
Internal & Lifestyle Factors
- Chronic stress
- Poor sleep quality
- Nutrient-deficient diet
- Skin conditions like eczema, rosacea, or psoriasis
Aggressive skincare routines are the most common cause.
Can Active Ingredients Damage the Skin Barrier?
Yes. Overuse of actives can compromise barrier integrity.
Ingredients like retinoids, exfoliating acids, and even vitamin C can damage the barrier when:
- Used too frequently
- Layered incorrectly
- Applied to already-damaged skin
Barrier repair should always come before active treatments.
➡️ Niacinamide for Skin Barrier Repair
➡️ Over-Exfoliation: Signs, Causes, and Recovery
How Long Does It Take to Repair a Damaged Skin Barrier?
With consistent, gentle care:
- Mild damage: 1-2 weeks
- Moderate damage: 2-4 weeks
- Severe damage: longer, depending on skin condition
There is no overnight fix. Skin biology doesn’t work that way.
Best Ingredients for Skin Barrier Repair
Barrier repair focuses on restoring lipids, hydration, and calm.
Essential Barrier Ingredients
Ceramides
Rebuild the lipid matrix and reduce moisture loss.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
Strengthens the barrier, improves hydration, and reduces inflammation.
Panthenol (Provitamin B5)
Soothes irritation and accelerates repair.
Fatty Acids (Omega-3 & Omega-6)
Support lipid balance and barrier strength.
Squalane
Mimics natural skin oils and prevents dehydration.
Supporting Ingredients
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Colloidal Oatmeal
- Vitamin E
- Prebiotics and Postbiotics
- Peptides and skin-identical lipids
➡️ Ceramides Explained: Types, Benefits, and Usage
Skin Barrier Repair Routine (Morning & Night)
Morning Routine
- Gentle Cleanser – low-pH, fragrance-free
- Hydrating Serum – hyaluronic acid or niacinamide
- Barrier Moisturizer – ceramides, squalane, fatty acids
- Mineral Sunscreen – zinc oxide or titanium dioxide
Night Routine
- Gentle Cleanser
- Barrier Repair Treatment – panthenol or ceramides
- Nourishing Moisturizer or Occlusive
- Optional hydrating mask (1–2× weekly)
What to Avoid Temporarily
- Retinoids
- Chemical exfoliants
- Strong vitamin C
- Fragrance and alcohol
Why Barrier-First Skincare Is a 2026 Trend
- Searches for “skin barrier repair” have increased by 29% year-over-year
- Consumers are shifting away from aggressive routines
- Ceramides, panthenol, and niacinamide dominate modern formulations
- Microbiome-friendly skincare is gaining traction
This is not a fad. It’s a correction to years of over-exfoliation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Signs include dryness, redness, burning sensations, sensitivity, and breakouts after using products that previously worked fine.
Yes. Niacinamide helps increase ceramide production, reduce inflammation, and improve hydration when used consistently.
Pause actives for at least 2–4 weeks or until stinging, redness, and sensitivity resolve.
Yes. A damaged barrier can cause excess oil production and worsen acne.
Only if they contain barrier-repair ingredients like ceramides, fatty acids, and cholesterol.
About Author
Written by GlowNest Care Editorial Team
GlowNest Care is a skincare education platform focused on science-backed routines, ingredient transparency, and long-term skin health. Our content is researched using dermatological studies, clinical guidelines, and real-world skincare experience.